Plant Based Protein Under 2025’s Spotlight: What Works and What’s Hype
Introduction: The Plant Based Protein Boom
In 2025, plant based protein isn’t just a niche trend—it’s a global movement. From eco-conscious consumers to athletes seeking cleaner nutrition, more people are swapping animal-based proteins for plant-powered alternatives.
But with this surge in popularity comes a flood of products, from protein powders to meat alternatives, each promising exceptional health benefits. The question is—which plant based proteins genuinely work, and which are just marketing hype? And how can nutritional & supplements fit into the picture for a balanced, effective approach?
Why Plant Based Protein Is Gaining Ground
Several factors have propelled plant based protein into the spotlight:
- Environmental Concerns: Lower carbon footprint compared to animal agriculture.
- Health Benefits: Linked to lower cholesterol, reduced inflammation, and improved heart health.
- Ethical Choices: Growing awareness of animal welfare issues.
- Dietary Trends: Vegan, vegetarian, and flexitarian diets are more mainstream than ever.
The plant based market is now rich with options—some excellent, others heavily processed and lacking nutritional value.
The Nutritional Science of Plant Based Protein
Protein is made up of amino acids, nine of which are essential because the body cannot produce them. Complete proteins contain all nine essential amino acids, while incomplete proteins lack one or more.
Most plant based proteins are incomplete on their own, but strategic food combinations—like rice and beans or hummus with whole grain pita—can provide all essential amino acids. Certain sources, like soy, quinoa, and hemp, are naturally complete.
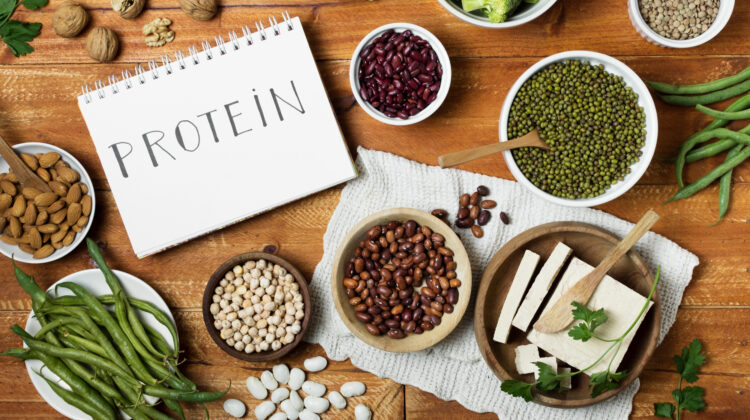
What Works: Proven Plant Based Protein Sources
1. Lentils and Legumes
- Benefits: High in protein, fiber, and iron.
- Best Use: Soups, salads, and stews for a hearty protein boost.
2. Soy (Tofu, Tempeh, Edamame)
- Benefits: Complete protein with all essential amino acids; versatile in cooking.
- Best Use: Stir-fries, curries, or grilled for sandwiches and wraps.
3. Quinoa
- Benefits: Gluten-free complete protein; rich in magnesium and fiber.
- Best Use: Salad base or side dish in place of rice.
4. Hemp Seeds
- Benefits: Complete protein plus omega-3 fatty acids.
- Best Use: Sprinkled over smoothies, salads, or oatmeal.
5. Chia and Flax Seeds
- Benefits: Contain protein, healthy fats, and fiber; support digestive health.
- Best Use: In smoothies, puddings, or baked goods.
6. Pea Protein
- Benefits: Popular in plant based protein powders; hypoallergenic.
- Best Use: Blended into shakes or baked into high-protein snacks.
What’s Mostly Hype: Marketing Over Substance
While many plant based protein options are beneficial, some are more hype than help:
- Highly Processed Meat Substitutes: Some contain excessive sodium, additives, and refined oils that offset health benefits.
- Protein-Enriched Snack Foods: Chips, cookies, and candies with added protein may still be high in sugar, unhealthy fats, or artificial ingredients.
- Overpriced “Superfood” Powders: Not all blends deliver meaningful protein per serving; always check the nutrition label.
The Role of Nutritional & Supplements
Even with a plant based diet rich in whole foods, nutritional & supplements can help meet specific health needs:
- Plant Based Protein Powders: Convenient for athletes, busy professionals, or those with higher protein requirements.
- B12 Supplements: Critical for plant based eaters since B12 is primarily found in animal products.
- Omega-3 from Algae: A sustainable alternative to fish oil for heart and brain health.
- Iron Supplements: Especially useful for individuals with increased iron needs or low dietary intake.
When recommending supplements as an affiliate, focus on quality—look for products with clean ingredient lists, third-party testing, and transparent sourcing.
How to Maximize Plant Based Protein Intake
1. Combine Protein Sources
Pair incomplete proteins to create a complete amino acid profile—for example, lentils with whole grains or nut butter on whole grain toast.
2. Spread Protein Across Meals
Aim for 15–25 grams per meal instead of loading all your protein into one shake.
3. Use Whole Foods First
Supplements should support, not replace, nutrient-rich foods like legumes, seeds, and grains.
4. Watch Portion Sizes
Some plant based proteins, like nuts and seeds, are calorie-dense; balance is key.
5. Read Labels Carefully
Choose products with minimal processing, low sodium, and no unnecessary additives.
Health Benefits of Balanced Plant Based Protein
When done right, incorporating plant based protein can:
- Support muscle repair and growth.
- Improve heart health by lowering saturated fat intake.
- Enhance digestion with fiber-rich sources.
- Provide sustainable, long-lasting energy.
Affiliate Marketing Opportunity: Turning Education into Action
For a health and wellbeing affiliate website, the plant based protein boom offers many product pairing possibilities:
- Protein Powders: Promote pea, hemp, soy, or blended plant based protein powders.
- Meal Kits: Partner with plant based meal delivery services.
- Nutritional & Supplements: B12, vegan omega-3, and iron supplements.
- Kitchen Tools: High-speed blenders, food processors, and meal prep containers.
By providing valuable educational content alongside product recommendations, you position yourself as a trusted guide—not just a seller.
Conclusion: Navigating the Plant Protein Landscape in 2025
Plant based protein offers incredible health, environmental, and ethical benefits—but not all products are created equal. Focus on whole food sources, use nutritional & supplements strategically, and avoid falling for marketing hype that prioritizes packaging over nutrition.
In 2025, the smartest approach is a balanced one—leveraging proven plant based proteins for your core nutrition while using supplements to fill gaps. With the right knowledge and choices, plant based eating can be both nourishing and sustainable for the long haul.